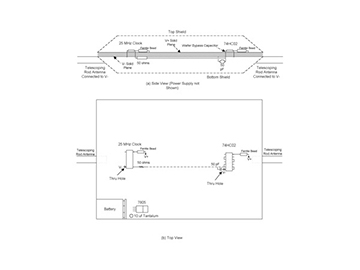
By attaching antennas to a printed circuit board we can analyze the physics of unwanted radiation

The biconical antenna can be modeled using simple and inexpensive software tools

Jeffrey Davis’ innovative design for a device driver lowers emissions without compromising performance

As a signal trace is moved towards the edges of a return plane, the inductance of the return plane rises

Flux from a signal conductor can loop around a return conductor inducing a voltage along it

A plane wave impinging on a metal shield with an aperture emerges as a point source

The pyramidal absorbers can be modeled as a sandwich of planes with varying resistivity

A map of vector potential from a small wire element

A return plane can develop a voltage along its length causing attached cables to radiate

A slot cut across a solid return plane can cause havoc because of its affect on return inductance

“Lost Flux," --the flux created by the center conductor that leaks around a shield -- causes the shield to radiate
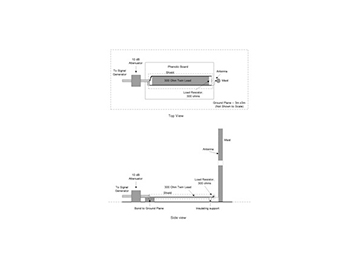
Common mode currents are created when balanced geometries meet unbalanced ones”

Divergence -- the flux flowing into and out of a small volume element -- is a key concept in field theory

A small change in an electric field over distance creates a changing magnetic field at right angles to it

Varying signal and return geometries radiate differently due to varying amounts of "lost flux"